Ex 3C
Numericals
1. Mass of the body, m = 5kg
Velocity, v = 2 m/s
Linear momentum = mv = 5 x 2 kg m/s = 10 kg m/s
2. Linear momentum = 0.5 kg m/s
Mass, m = 50 g = 0.05 kg
Velocity = Linear momentum/mass = 0.5/0.05 m/s = 10 m/s
3. Force, F = 15 N
Mass, m = 2 kg
Acceleration, a = F/m [ From Newton's second law]
a = (15/2) ms-2 = 7.5 ms-2
4. Force, F = 10 N
Mass, m = 5 kg
Acceleration, a = F/m [ From Newton's second law]
a = (10/5) ms-2 = 2 ms-2
5. Mass, m = 0.5 kg.
Acceleration, a = 5 ms-2
Force, F = ma [ From Newton's second law]
F = 0.5 x 5 N = 2.5 N.
6. Force, F = 10 N
Mass, m = 2 kg
Time, t = 3 s
Initial velocity, u = 0 m/s.
(i) Let v be the final velocity acquired.
From Newton's second law, F = ma.
a = F/m = 10/2 = 5 ms-2.
From the 1st equation of motion,
v = u+ at
v = 0 + 5 x 3 = 15 m/s.
(ii) Change in momentum = Final momentum - initial momentum
△p = mv - mu.
△p = m (v-u).
△p = 2 ( 15-0) = 30 kg m/s.
7. Mass, m = 100 kg
Distance moved, s = 100 m
Initial velocity, u = 0
(i) Because the body moves through a distance of 100 m in 5 s,
Velocity of the body = Distance moved / time taken
Velocity = (100/5) = 20 m/s
(ii) From Newton's third equation of motion,
v2 =u2 + 2as.
a = (v2 -u2) /2s.
a = [ (202 - 02)/ 2(100) ] ms-2 = 2 ms-2.
(iii) Force, F = ma
F = 100 x 2 N = 200 N.
8. Slope of a velocity-time graph gives the value of acceleration.
Here, slope = 20/5 = 4 m/s2.
acceleration, a = 4 m/s2.
F = MA
Given mass, m = 100 g = 0.1 kg.
Force = 0.1 x 4 = 0.4 N.
9. Mass, m = 2 kg
Initial velocity, u = 0
Final velocity, v = 2 m/s
Time, t = 0.1 s
Acceleration = Change in velocity/time
a = (v - u) /t
a = (2 - 0)/ 0.1 = 20 ms-2.
Force = Mass Acceleration
F = 2 x 20 = 40 N.
10. Mass, m = 100 g = 0.1 kg.
Initial velocity, u = 30 m/s.
Final velocity, v = 0.
Time, t = 0.03 s.
Acceleration = Change in velocity/time.
a = (v - u)/t.
a = (0 - 30)/ 0.03 = -1000 ms-2.
Negative sign indicates retardation.
Now, Force = Mass Acceleration
F = 0.1 x 1000 = 100 N.
Initial velocity, u = 54 km/hr = 15 m/s.
Final velocity, v = 0.
Time, t = 10 s.
Acceleration = Change in velocity/time.
a = (v - u)/t.
a = (0 - 15)/10 = -1.5 ms-2.
Negative sign indicates retardation.
Now, Force = Mass Acceleration
F = 480 x 1.5 = 720 N.
12. Mass, m = 50 gm = 0.05 kg.
Initial velocity, u = 100 m/s.
Final velocity, v = 0.
Distance, s = 2 cm = 0.02 m.
(i) Initial momentum = mu = 0.05 x 100 = 5 kg m/s.
(ii) Final momentum = mv = 0.05 x 0 = 0 kg m/s.
(iii) Acceleration, a = (v2 - u2)/2s.
a = (02 - 1002)/ 2 x 0.02 = -2.5 x 105 ms-2.
Therefore, retardation is 2.5 x 105 ms-2.
(iv) Force, F = ma
F = 0.05 x 2.5 x 105 = 12500 N
13. Let the force be F.
Force F causes an acceleration, a = 10 m/s2 in a body of mass, m = 500 g or 0.5 kg
Thus, F = ma
F = 0.5 x 10 = 5 N
Let a' be the acceleration which force 5N cause on a body of mass, m' = 5 kg.
Then, a' = F/m'.
a' = (5/5) ms-2 = 1 ms-2.
14. Initial velocity, u = 30 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0
Time, t = 2 s
Force, F = 1500 N
Here, a = (v - u)/t = (0 -30)/ 2 = -15 ms-2.
Negative sign indicates retardation.
Now, F = ma.
m = F/a = (1500/ 15) = 100 kg.
(a) Change in momentum = Final momentum - Initial momentum
△p = m (v - u)
△p= 100 (0 - 30)
△p= 3000 kg m/s
(b) Acceleration, a = (v - u)/t.
a = (0 - 30)/ 2 = -15 ms-2,
Negative sign indicates retardation.
Thus, retardation = 15 ms-2.
(c) From Newton's second law of motion,
F = ma
m = F/a = (1500/ 15) = 100 kg.
Numericals
Ex 3D
Ex 3E
Numericals
1. Force of attraction between two bodies = 10 N
If the new distance R'= R/2, then let F' be the force acting between the bodies. Then:
2. Weight = mg
W = 5 x 9.8 = 50 N.
3. Mass = 10 kg
(i) Weight (in kgf) = 10 x 1 kgf = 10 kgf (1 kgf = 9.8 N)
(ii) Weight (in newton) = 10 x 9.8 = 98 N.
4. Mass = 5 kg.
g = 9.8 m/s2.
Let F be the force of gravity,
F = mg.
F = 5 x 9.8 = 49 N.
Force of gravity always acts downwards.
5. Weight, W = 2.0 N
g = 9.8 m/s2
Let 'm' be the mass of the body.
W = mg
m = W/g = (2/9.8) kg = 0.2 kg.
6. Weight of the body on Earth = 98 N.
Acceleration due to gravity on Earth = 9.8 m/s2.
Let 'm' be the mass of the body on Earth.
m = W/g
m = (98/9.8) = 10 kg
Thus, the mass of the body is 10 kg, which always remains constant.
(a) Mass on moon = mass on Earth = 10 kg
(b) Let weight on moon is W'.
W' = mass 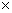 acceleration due to gravity on the Moon.
acceleration due to gravity on the Moon.
W' = 10 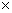 1.6 =16 N.
1.6 =16 N.
7. Man's weight on Earth = 600 N
Man's weight on the Moon = (1/6) man's weight on Earth;
Because the acceleration due to gravity on the Moon is 1/6th that of Earth and w = mg.
Therefore, man's weight on Moon = (600/6) = 100 N.
8. Mass, m = 10.5 kg
G = 10 m/s2
(a) Force, F = mg
F = 10.5 x 10 = 105 N
(b) Weight, w = mg
w = 10.5 x 10 = 105 N
9. Let 'S' be the height.
Time taken, t = 3 s
g = 9.8 m/s2
Initial velocity, u = 0
(a) Using the second equation of motion,
S = ut + (1/2) gt2
S = 0 + 1/2 x 9.8 x 3 x 3 = 44.1 m
(b) Let 'v' be the velocity with which the ball strikes the ground.
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 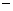 u2 = 2gs
u2 = 2gs
v2 - 02 = 2 x 9.8 x 44.1 = 864.36
v = 29.4 m/s
10. Mass, m = 5kg
Force, F = mg
F = 5 x 9.8 = 49 N
11. Given, maximum height reached, s = 20 m
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2
(i) Let 'u' be the initial velocity.
At the highest point, velocity = 0
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 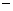 u2 = 2gs
u2 = 2gs
0  u2 = 2 x 10 x 20 m/s
u2 = 2 x 10 x 20 m/s
u2 =  400 m/s (Negative sign indicates that the motion is against gravity)
400 m/s (Negative sign indicates that the motion is against gravity)
u = 20 m/s
(b) Let v' be the final velocity of the ball on reaching the ground.
Considering the motion from the highest point to ground,
Velocity at highest point = 0 = Initial velocity for downward journey of the ball.
Distance travelled, s = 20m
Using the third equation of motion,
v2  u2 = 2gs
u2 = 2gs
v2  0 = 2 x10 x 20 m/s
0 = 2 x10 x 20 m/s
v2 = 400 m/s
v = 420 m/s
(c) Now total time for which the ball remains in air, t = 2u/g.
t = 2 x 20 x 10
t = 4s.
12. Initial velocity u = 0
12. Initial velocity u = 0
Final velocity = 20 m/s
g = 10 m/s2
Let 'h' be the height of the tower.
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 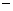 u2 = 2gs
u2 = 2gs
202 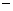 0 = 2 x 10 x h
0 = 2 x 10 x h
h = 400 / 20 =20 m
13. Total time of journey = 6 s
g = 10 m/s2
(i) Let 'H' be the greatest height.
Time of ascent, t = 6/2 = 3 s,
For ascent, initial velocity, u = 0
Using the second equation of motion,
H = ut + (1/2) gt2
H = 0 + 1/2 x 10 x 32 = 45 m
(ii) Let u' be the initial velocity.
Final velocity, v = 0
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2gH
v2 - 0 = 2 x 10 x 45 , v2 = 900
v = 30 m/s
14. Initial velocity, u = 20 m/s
Time, t = 2s
g = 10 m/s2
Maximum height reached in 2s, H = (1/2) gt2
H = 1/2 x 10 x 22 = 20 m
15. (a) Height, s = 80m
g = 10 m/s2
Using the second equation of motion,
S = ut + (1/2) gt2
80 = 0+ 1/2 x 10 x t2
t 2 = 16
t = 4s
(b) Let 'v' be the velocity on reaching the ground.
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2gH
v2 - 0 = 2 x 10 x 80
v2 = 1600
v = 40 m/s
16. Time t = 2.5
g = 9.8 m/s2
Height, H = (1/2) gt2
H = 1/2 x 9.8 x 2.52
H = 30.6 m
17. Initial velocity, u = 49 m/s
g = 9.8 m/s2
(i) Let H be the maximum height attained.
At the highest point, velocity = 0.
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2 x g x H
0 - 492 = 2 x -9.8 x H
H = 492 / 19.6 = 122.5 m
(ii) Total time of flight is given by t = 2u/g
t = 2 x 49 / 9.8 = 10 s
18. Initial velocity u = 0
Time t = 4 s
g = 10 m/s2
Let 'H' be the height of the tower.
Using the second equation of motion,
H = ut + (1/2) gt2
H = 0 + 1/ 2 x 10 x 42 = 80 m
19. (i) Time t =20 s
g = 10 m/s2
Let 'D' be the depth of the well.
Using the second equation of motion,
D = ut + (1/2) gt2
D = 0 + 1/2 x 10 x 202 = 2000 m
(ii) Speed of sound = 330 m/s
Depth of well = 2000 m
Time taken to hear the echo after the pebble reaches the water surface = Depth/speed
= (2000/330) s = 6.1 s
Time taken for pebble to reach the water surface = 20 s.
Therefore, the total time taken to hear the echo after the pebble is dropped = 20 + 6.1 = 21.6 s.
20 Let x be the height of the tower.
Let h be the distance from the top of the tower to the highest point.
Initial velocity u = 19.6 m/s
g = 9.8 m/s2
At the highest point, velocity = 0
Using the third equation of motion,
v2 - u2 = 2gh
-(19.6) 2 = 2 x -9.8 x h
h = 19.6 m
If the ball takes time t1 to go to the highest point from the top of building, then for the upward
journey from the relation, v = u - gt,
journey from the relation, v = u - gt,
0 = 19.6 - 9.8 x t1 = 2s
(ii) Let us consider the motion for the part (x+h)
Time taken to travel from highest point to the ground = (5 - 2) = 3s
Using the equation s = ut + (1/2) gt2
We get, (x + h) = 0 + 1/2 x 9.8 x 32
(x + 19.6) = 44.1 m
x = 44.1 - 19.6 = 24.5 m
Thus, height of the tower = 24.5 m
(iii) Let v be the velocity of the ball on reaching the ground.
Using the relation, v = u + gt
We get: v = 0 + 9.8 x 3 = 29.4 m/s


